GDA Nursing Class Notes 22
POSITIONING
Positioning defined as placing the patient in such a way to perform therapeutic intervention to promote the health.
Positioning a patient is a crucial aspect of healthcare, especially in medical settings such as hospitals, clinics, and during various medical procedures. Proper positioning ensures patient comfort, safety, and accessibility for healthcare providers. The specific positioning depends on the patient’s condition, the procedure being performed, and the healthcare setting.
BODY POSITIONS
Body positions refer to the different ways in which the human body can be arranged or oriented in space. These positions are often used in healthcare, sports, fitness, dance, and various therapeutic and medical contexts.
PRONE POSITION
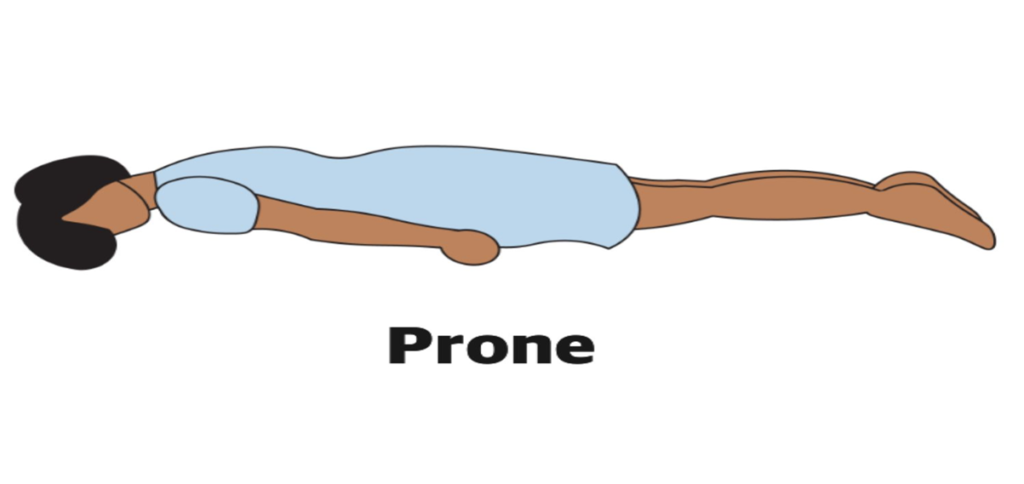
The prone position is a body position in which a person lies flat on their stomach with their face down and their back up. This position is commonly used in medical settings for various purposes, including medical examinations, surgical procedures, and respiratory management.
Used in spinal surgery, and rescue therapy for ARDS patients.
SUPINE POSITION
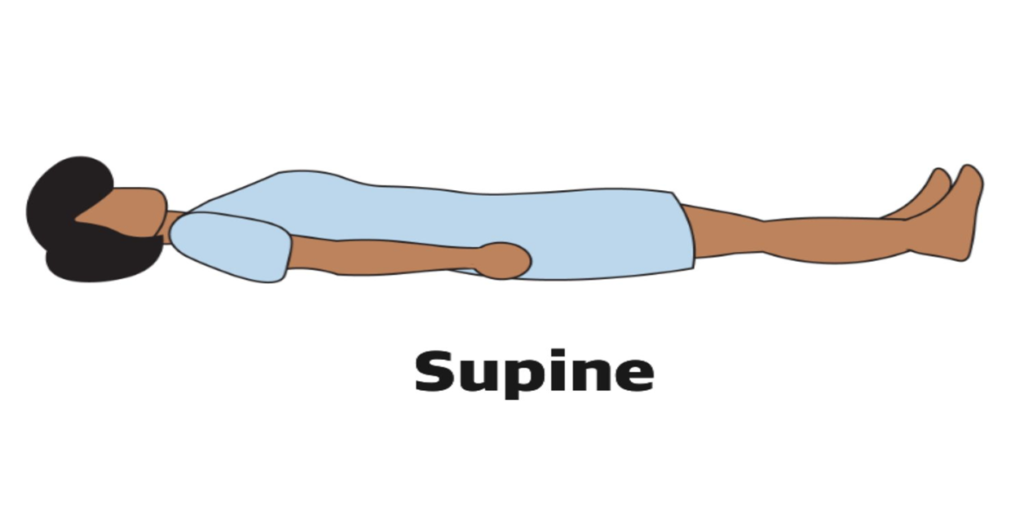
The supine position is a body position in which a person lies flat on their back with their face upward and their abdomen facing the ceiling. It is one of the most common and widely used positions in medical examinations, surgical procedures, and patient care.
Used for general examination and physical examination, and different chest and abdominal surgery.
LATERAL POSITION
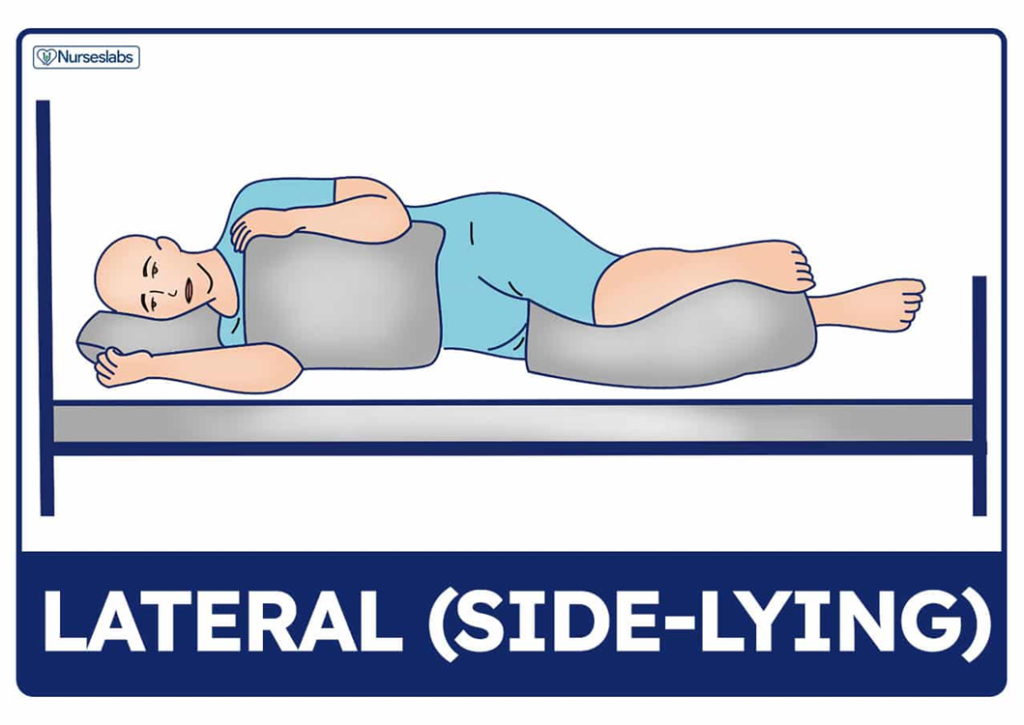
The lateral position is a body position in which a person lies on their side with their body forming a straight line. It is a common position used in various healthcare and medical settings, as well as for sleeping and relaxation.
Used during back, kidney and hip surgery.
DORSAL RECUMBENT POSITION
The dorsal recumbent position is a body position in which a person lies flat on their back with their knees flexed and their feet flat on the bed or examination table. This position is commonly used in medical examinations, procedures, and patient care.
Used for catheterization

LITHOTOMY POSITION
The lithotomy position is a medical body position in which a patient lies on their back with their legs flexed at the hips and knees, and their feet placed in stirrups. This position is widely used in gynecological, urological, and some colorectal examinations and procedures.
Used during childbirth and surgery in pelvic area.

SIMS POSOTION
The Sims position, also known as the left lateral position, is a specific body position in which a person lies on their left side with their lower arm positioned behind them and their upper knee flexed. This position is commonly used in healthcare for various purposes, including medical examinations, procedures, and enema administration.
Used for rectal examination, treatment, and vaginal examining.

TRENDELENBURG POSITION
The Trendelenburg position is a medical body position in which a patient is placed on their back on an incline with the head positioned lower than the feet. This position is named after the German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg and is used for various medical purposes.
Used in lower abdominal surgery.

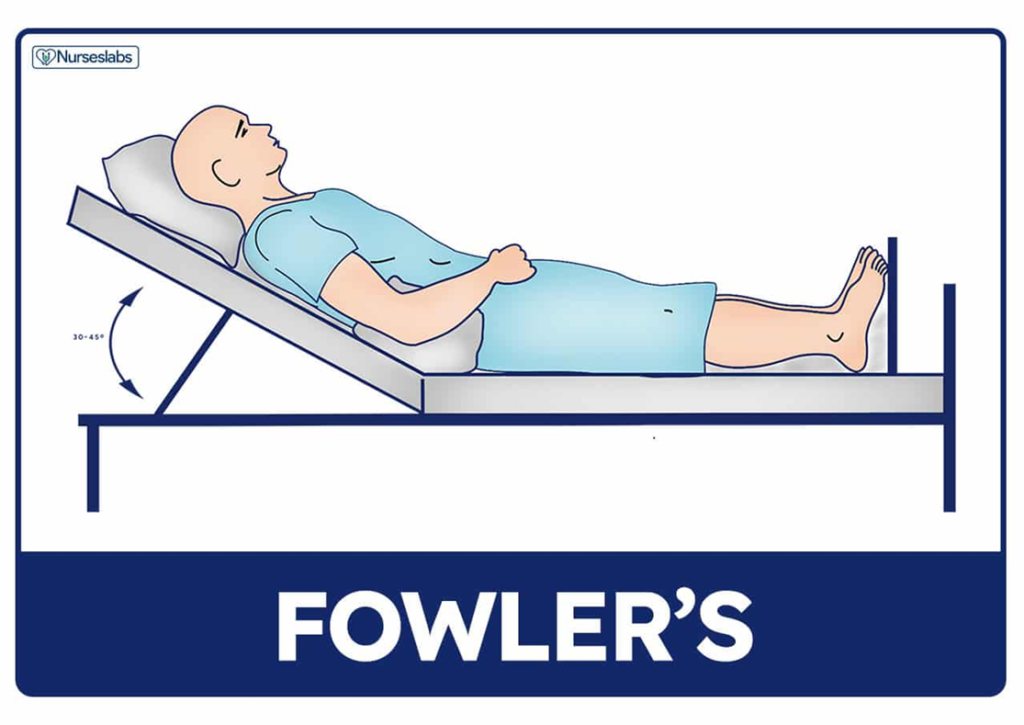
FOWLER’S POSITION
Fowler’s position is a medical body position in which a patient is seated in a semi-upright position, typically at an angle of 45 to 60 degrees from horizontal. This position is widely used in healthcare for various purposes and is named after the American surgeon George Ryerson Fowler.
To combat respiratory distress.
ORTHOPNEIC POSITION
The orthopneic position is a specific body position used by some individuals with respiratory difficulties, particularly those with conditions like congestive heart failure (CHF), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or severe respiratory distress.
Useful for maximum lung expansion.

