GDA Nursing Class Notes 30
CELL

•Cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms.
•They are the smallest independently functioning units in the body of an organism and are often referred to as the “building blocks of life.
•” Cells are capable of carrying out a variety of processes necessary for life, including growth, reproduction, energy production, and responding to their environment.
CELL DIVISION

•Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells, each of which inherits a portion of the parent cell’s genetic material.
• Cell division is a fundamental process in the growth, development, repair, and reproduction of multicellular organisms.
Mitosis
•There are two main types of cell division:
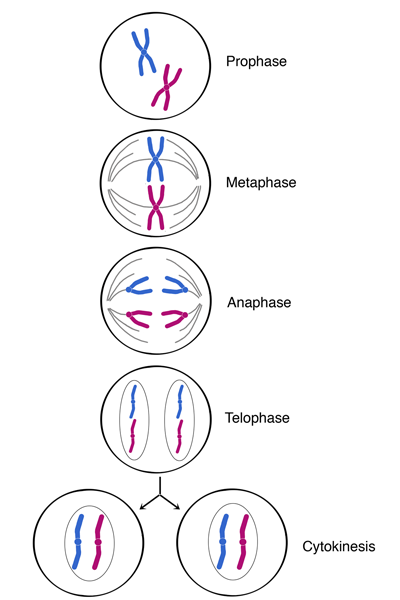
•Mitosis is the type of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It plays a crucial role in growth, tissue repair
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms. It results in the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell.

TISSUE
•Tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function that work together to perform specific tasks within an organism.
In multicellular organisms like humans, tissues are organized into various types, each specialized for particular functions.

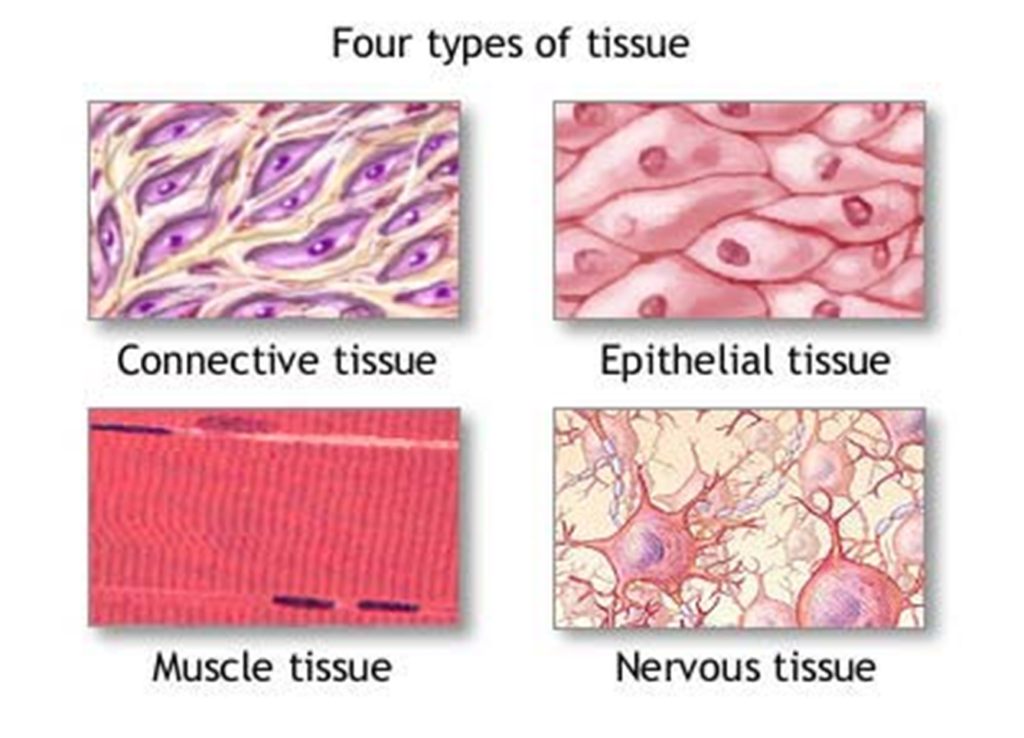
•TYPES OF TISSUES
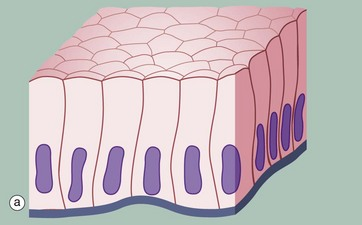
•Epithelial Tissue: This tissue covers the surfaces of the body, both externally and internally. Epithelial tissue can be found in the skin, lining of organs, and various other body surfaces.
•Connective Tissue: Connective tissue provides support, structure, and connection between different tissues and organs. It includes a wide range of tissues such as bone, cartilage, blood, adipose (fat), and fibrous connective tissues.

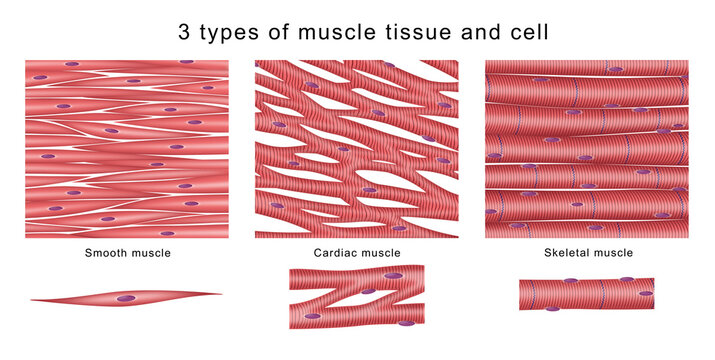
•Muscle Tissue: Muscle tissue is responsible for movement and contractility. There are three types of muscle tissue:
•Skeletal Muscle: Attached to bones and responsible for voluntary movement.
•Smooth Muscle: Found in the walls of organs and blood vessels, involved in involuntary movements.
•Cardiac Muscle: Forms the heart and contracts to pump blood.
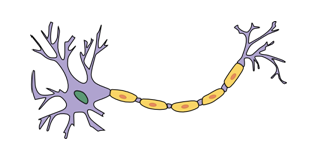
•Nervous Tissue: Nervous tissue is composed of neurons (nerve cells) and supporting cells. It’s responsible for transmitting and processing information through electrical signals. Nervous tissue forms the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.