GDA Nursing Class Notes 39
FEEDING

The term “feeding” in the context of patient care refers to the process of providing nutrition to individuals who are unable to meet their dietary needs through regular oral intake. This can include various methods, such as oral feeding, enteral feeding (using a tube that goes directly into the digestive system), or parenteral nutrition (administering nutrients intravenously). The goal of feeding a patient is to ensure they receive the necessary nutrients, calories, and fluids to support their health and well-being, especially when they have medical conditions that affect their ability to eat or digest food normally.
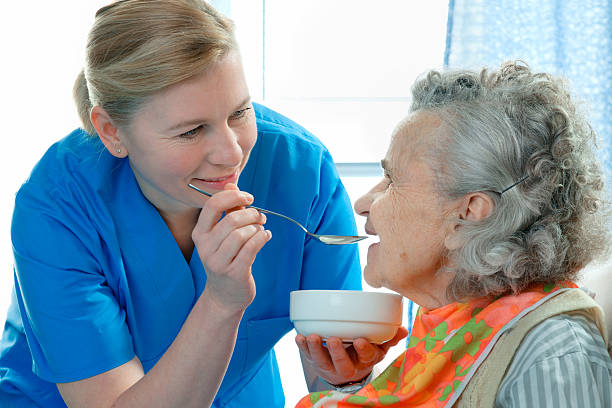
FEEDING THE HELPLESS PATIENT
•It is assisting a dependent patient to take food and fluids.
•To assist the patient to eat meal
•To improve nutritional status
•To prevent dehydration.
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS

•The diet is prescribed by the doctor, planned by the dietitian and implemented by the nurse.
•Food should be given at the correct time
•Maintain an intake output chart
•Food should not be too hot or too cold
•Wipe the patient’s mouth and chin whenever necessary
•Wash patient’s hand and mouth after meal.
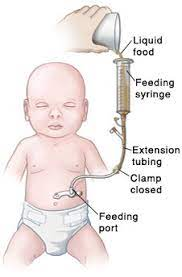
NASOGASTRIC TUBE FEEDING

•It is a method of introducing a tube through nose into stomach.
•It is also known as gastric gavages
•To provide large amount of fluid
•To provide adequate amount of nutrition
GASTROTOMY FEEDING\

•Gastrostomy feeding involves the insertion of a feeding tube directly into the stomach through a small incision in the abdomen.
•This procedure is performed when a person is unable to take in adequate nutrition orally and requires a more stable and long-term method of feeding.
•Gastrostomy feeding is often considered for individuals who have difficulty swallowing, are at risk of aspiration, or have conditions that prevent them from obtaining sufficient nutrients through regular eating.
INDICATION
•Unconscious and semiconscious patient
•After certain surgery of mouth and throat
•Patient unable to swallow
•Patient unable to retain the food