GDA Nursing Class Notes 23
TRANSFER OF PATIENT
Transfer is the movement of a patient to hospital or from one room to another, within the unit, or from one unit to another of the hospital, or from one hospital to another or to car ambulance.
The transfer of a patient refers to the process of moving a patient from one location to another within a healthcare facility or between healthcare facilities. This transfer can occur for various reasons, including medical treatment, diagnostic procedures, specialized care, or discharge. Proper patient transfer is crucial to ensure the safety, comfort, and well-being of the patient.
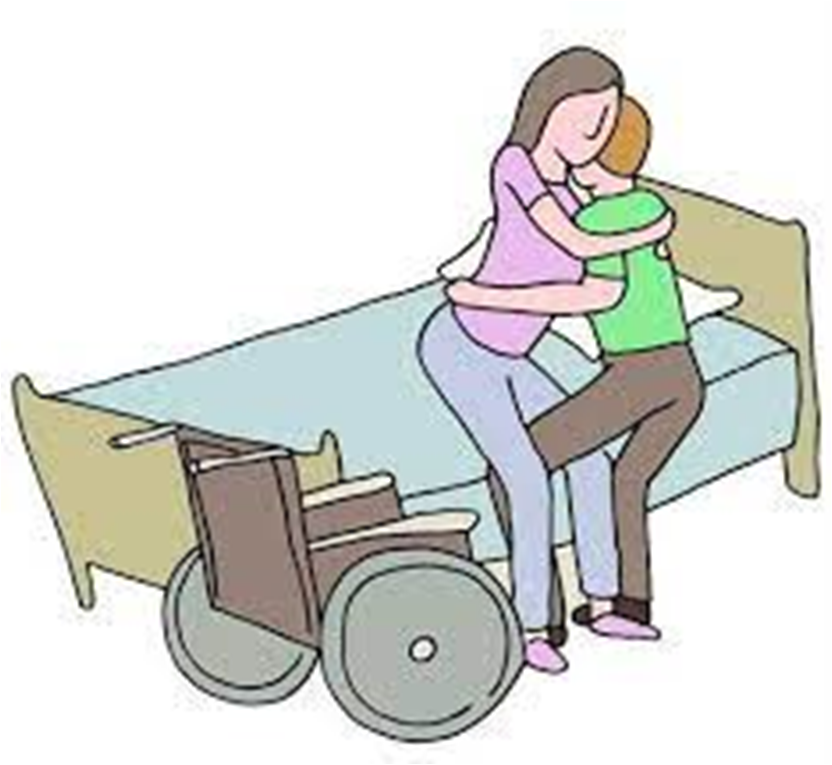
REASON FOR TRANSFER
•Change in patient condition
•Patient scheduled for surgery
•Patient requests transfer
•For isolation
•For diagnostic procedure

TYPES OF TRANSFER
•TRANSFER WITHIN THE HOSPITAL
•TRANSFER OUTSIDE OF THE HOSPITAL

LEVELS OF TRANSFER
•Independent transfer: Independent transfer means that a person can perform activities related to transferring themselves, such as moving from a bed to a wheelchair, getting in and out of a chair, or going from a sitting to a standing position without relying on the assistance of others.
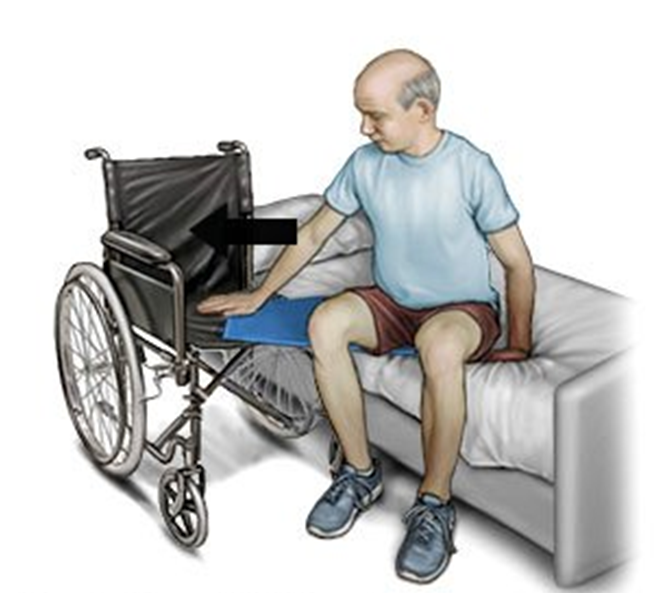
•Assisted transfer: An assisted transfer refers to a situation in which a patient or individual requires help and support from healthcare providers, caregivers, or assistive equipment to move from one location to another. This assistance is necessary when the person does not have the physical ability or strength to perform the transfer independently. Assisted transfers are common in healthcare settings and home care for individuals with varying degrees of mobility impairment.

•Dependent transfer: A dependent transfer is a type of patient or individual transfer in which the person being transferred has limited or no ability to participate actively in the transfer process. In a dependent transfer, healthcare providers or caregivers take on the primary responsibility for moving and positioning the individual. This type of transfer is necessary when the person lacks the physical or cognitive capacity to assist in their own movement.

EQUIPMENT
•Wheelchairs

•Trolley

•Gait belt
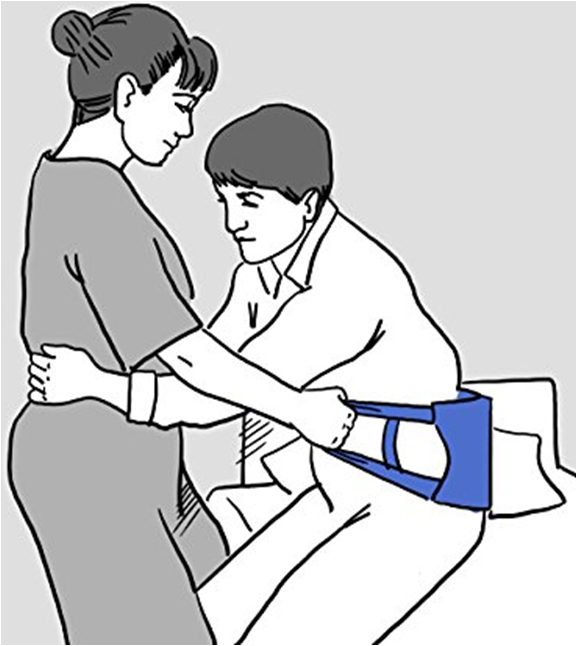
•Sliding board
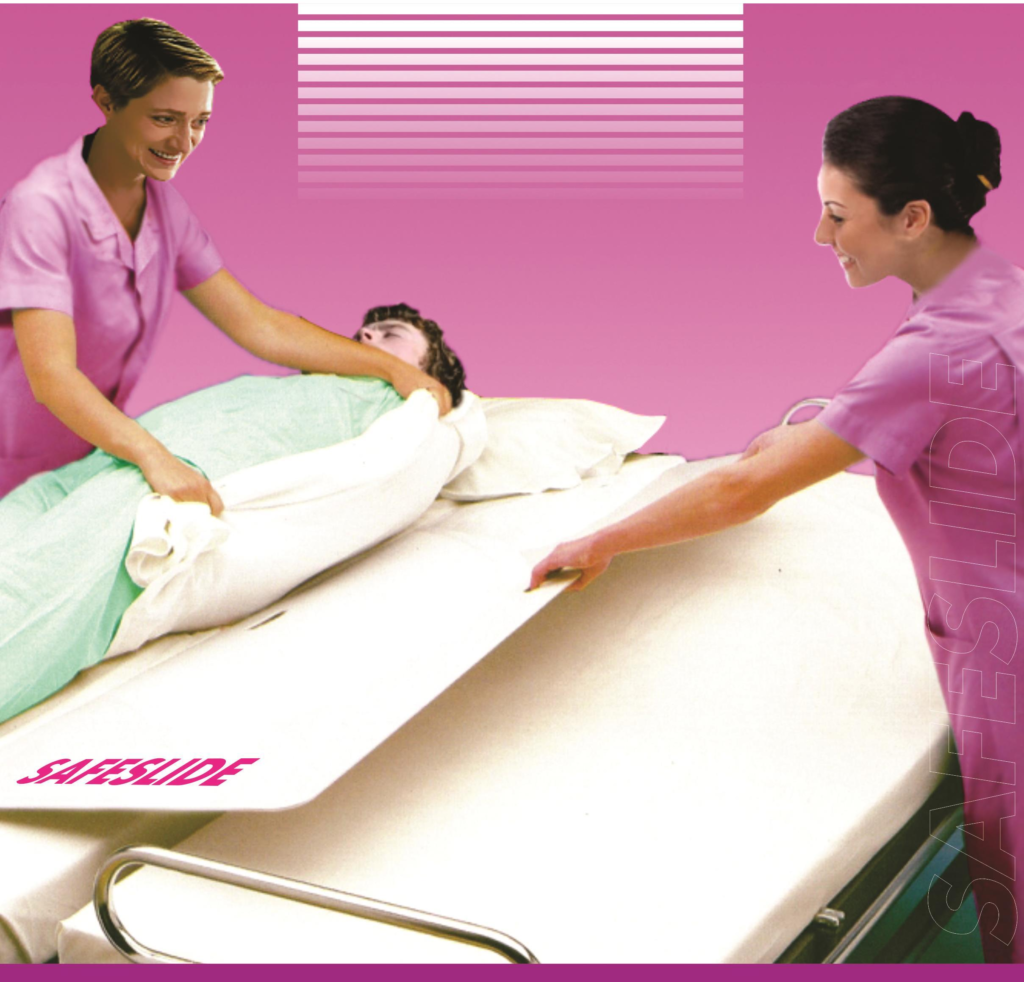
NURSING ROLE IN TRANSFER
1.Explain the procedure
2.Assess the patient condition
3.Explain about the equipment used
4.Make sure that the family members are notified of the patients transfer
5.Notify the receiving unit
6.Notify the admission department
7.Arrange for transportation
8.Help the patient to transfer
9.Explain about the condition and care plan of the patient to the receiving unit.
MOBILITY
Mobility is defined as the ability to move freely, easily in the environment.

NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
§ Assess the range of motion by asking the patient to move the selected body parts.
§ Assess the gait to check the balance and coordination of the body.
§ Assess the activity level of the patient to check the strength.
TERMINOLOGY
•FLEXION: The state of being bent

•EXTENSION: The state of being in straight line

•HYPEREXTENSION: The state of exaggerated extension

•ROTATION: Turning of a body part around the axis

•CIRCUMDUCTION: Rotating an extremity in a complete circle

