GDA Nursing Class Notes 26

NUTRITION
Nutrition refers to the process of acquiring, consuming, and utilizing food and nutrients by the human body to support growth, health, and overall well-being. It encompasses the intake of various substances, including macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats), micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), water, and dietary fiber. Proper nutrition is essential for the body’s growth, development, energy production, and maintenance of essential functions.
Nutrients
Nutrients are essential substances that the body requires to grow, develop, and maintain its health and overall function. They are obtained from the foods and beverages we consume and are crucial for various physiological processes. Nutrients can be broadly categorized into two main types: macronutrients and micronutrients.

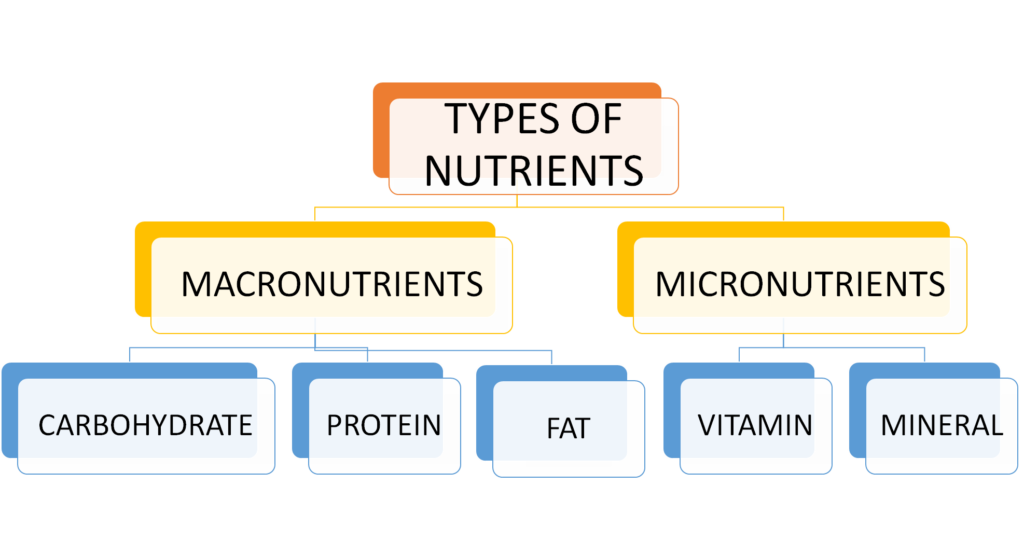
Macronutrients :- Macronutrients are nutrients that the body requires in relatively large amounts to provide energy and support various physiological functions.
The three main macronutrients are:
•Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. Good sources of carbohydrates include grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. They are broken down into glucose (sugar) and used for fuel.

•Proteins: Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues. Dietary sources of protein include meat, fish, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.

•Fats: Fats are important for energy storage, insulation, cushioning organs. Healthy sources of fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. Fats are a concentrated source of energy and are necessary for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K)

Micronutrients :- Micronutrients are nutrients that are needed in smaller amounts but are still essential for proper health and functioning. Micronutrients include vitamins and minerals:
•Vitamins: They are essential for metabolism, immune function, and overall well-being. Vitamins include vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin A, vitamins E , Vitamin K and vitamin B complex. Good sources are green leafy vegetables, fruits, etc. They are classified as water-soluble (e.g., vitamin C and the B vitamins) or fat-soluble (e.g., vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin K).

•Minerals: Minerals are inorganic elements that are necessary for bone health, nerve function, and fluid balance. Common minerals include calcium, iron, zinc, magnesium, and potassium. Dietary sources are dairy products, fruits, etc.

HYDRATION
Hydration refers to the process of maintaining an adequate balance of fluid and electrolytes in the body. It is crucial for various bodily functions, including temperature regulation, digestion, circulation, and overall well-being.
•Fluid: Fluid are liquids present in our body. The main fluid we intake is water. Water is a vital nutrient required for nearly every bodily function. It is essential for digestion, temperature regulation, waste elimination, and the transportation of nutrients and oxygen throughout the body. Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health.\

•Electrolytes are essential chemicals which play a crucial role in various physiological processes within the body. Electrolytes are present in body fluids such as blood, sweat, and urine. The major electrolytes in the human body include sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), chloride (Cl-), bicarbonate (HCO3-), and phosphate (PO43-).

DIET
Diet is the food or drink that a person consumes regularly. A diet refers to the pattern of food and beverages consumed regularly by an individual or a group of individuals. Diets can vary widely and may be influenced by cultural, regional, personal, and dietary preferences.

Balanced Diet: A balanced diet is one that provides all the necessary nutrients in the right proportions to maintain overall health. It typically includes a variety of foods from all food groups, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.

Therapeutic Diet: Therapeutic diets are prescribed by healthcare professionals to address specific medical conditions or health concerns. Examples include diabetic diets for managing blood sugar, gluten-free diets for individuals with celiac disease, and low-sodium diets for hypertension.

