GDA Nursing Class Note 15
Hospital Equipments
Hospital beds: Adjustable beds designed for patient comfort and medical care.
Features and Adjustments:
- Head and Foot Adjustments: Hospital beds allow for raising or lowering the head and foot sections, enabling patients to find a comfortable position for activities like reading or eating.
- Height Adjustment: Beds can be adjusted to different heights, making it easier for patients to get in and out of bed and facilitating caregiver access for providing care.
- Side Railings: Many hospital beds have side railings that can be raised or lowered to prevent patients from accidentally falling out of bed.
- Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg Positions: Some beds offer the ability to tilt the entire bed frame to assist with positioning patients for specific medical procedures or conditions.
- Wheels and Locks: Hospital beds are equipped with wheels, allowing for easy transportation within the facility. Wheel locks are essential to secure the bed in place when needed.
Hospital beds are an integral part of patient care, providing comfort, safety, and functionality for patients and caregivers. Different types of beds serve specific needs, and the features and adjustments vary, depending on the model and manufacturer.

Stretcher:
Purpose: Stretchers are used to transport patients who are unable to walk or require assistance during medical emergencies, surgeries, or when transferring between different areas of a healthcare facility.

Wheelchair:
Purpose: Wheelchairs are mobility aids designed for individuals who have difficulty walking or cannot walk independently. They provide support and enable users to move around comfortably.

Walker:
Purpose: Walkers are assistive devices designed to provide support and stability for individuals with mobility limitations. They assist users in maintaining balance while walking.These walkers have a simple frame with four legs and no wheels, providing the most stability but requiring the user to lift the walker with each step.

Dustbins in Hospitals:
- Purpose: Dustbins in hospitals serve as designated containers for the disposal of various types of waste generated within the healthcare setting.
- Waste Segregation: Hospitals follow specific waste management protocols that involve segregating waste into different categories, such as general waste, infectious waste, hazardous waste, sharps waste, and recyclable waste. Dustbins are typically labeled or color-coded to facilitate proper waste segregation.
- Types of Dustbins:
- General Waste Dustbins: These dustbins are used for non-infectious and non-hazardous waste, such as paper, food waste, and non-recyclable materials.
- Infectious Waste Dustbins: Dedicated bins for disposing of items contaminated with blood or bodily fluids, such as used dressings, gloves, and other medical waste.
- Sharps Waste Containers: Sharps containers are specifically designed for the safe disposal of needles, syringes, lancets, and other sharp medical instruments. These containers are puncture-resistant to prevent accidental injuries.
- Pharmaceutical Waste Bins: These bins are used to collect expired or unused medications and pharmaceutical products, ensuring proper disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
- Recycling Bins: Hospitals promote environmentally friendly practices by providing recycling bins for the proper disposal of recyclable materials like paper, plastic, and aluminum.

Oxygen Cylinder:
- Purpose: Oxygen cylinders are portable devices used to store and deliver medical-grade oxygen to individuals who require supplemental oxygen therapy.
- Composition and Safety:
- Oxygen: Oxygen cylinders contain compressed or liquid oxygen, which is a vital component for respiration and is administered to patients with respiratory conditions or low oxygen levels.
- Safety Precautions: Oxygen cylinders must be handled and stored with care. They should be kept upright, away from heat sources, and protected from physical damage. Smoking or open flames should be avoided near oxygen cylinders, as oxygen supports combustion and can increase the risk of fire.

Oxygen Mask:
Purpose: Oxygen masks are devices used to deliver oxygen directly to a patient’s respiratory system. They are commonly used in hospitals, emergency medical settings, and during certain medical procedures.
- Proper Fit: Oxygen masks should be properly fitted to ensure an airtight seal and efficient oxygen delivery. Healthcare professionals should assess and adjust the mask for individual patients.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Oxygen masks should be cleaned and maintained according to the manufacturer’s instructions to prevent contamination and ensure proper functioning.

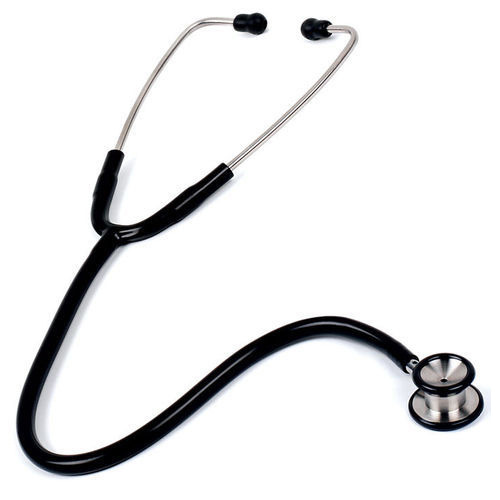
Stethoscope:
Purpose: A stethoscope is a medical device used by healthcare professionals to listen to internal sounds of the body, such as the heartbeat, lung sounds, and blood flow.
Usage and Technique:
- Proper Placement: The chestpiece of the stethoscope is placed on the patient’s skin over the area of interest, such as the chest for heart sounds or the back for lung sounds.
- Diaphragm vs. Bell: The diaphragm is used for high-frequency sounds, such as heart and lung sounds, while the bell is used for low-frequency sounds, such as murmurs or bruits.
- Earpiece Positioning: The earpieces should be properly inserted into the ears for optimal sound transmission and clarity.
- Background Noise: To minimize interference from external noise, it is best to auscultate in a quiet environment whenever possible.
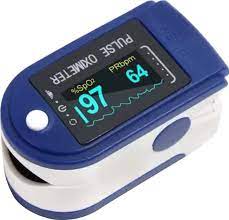
Pulse Oximeter:
Purpose: A pulse oximeter is a non-invasive medical device used to measure the oxygen saturation level in a person’s blood and their heart rate.
Functionality:
- Measurement Principle: Pulse oximeters work by emitting light wavelengths through a person’s skin and measuring the amount of light absorbed by oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): Pulse oximeters provide a numerical reading indicating the percentage of oxygen saturation in the blood.
- Pulse Rate: Pulse oximeters also measure the heart rate by analyzing the pulsatile nature of blood flow
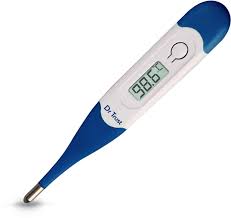
Thermometer:
Purpose: A thermometer is a device used to measure body temperature, helping to assess fever or hypothermia.
Usage and Measurement:
- Site Selection: Thermometers can be used orally, rectally, axillary (underarm), or tympanically (in the ear). Each site has its own considerations for accurate measurement.
- Safety and Hygiene: Proper cleaning and disinfection should be followed for thermometers to prevent cross-contamination between individuals.
- Measurement Accuracy: Thermometers should be used according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accurate temperature readings.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
