GDA Nursing Class Notes 7
SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION
A subcutaneous (SC) injection is a medical procedure in which a substance, typically a medication, is injected just beneath the skin into the fatty tissue. This route of administration allows for the relatively quick absorption of the substance into the bloodstream. Subcutaneous injections are commonly used for medications that need to be absorbed relatively quickly, such as insulin, certain vaccines, and other medications.
Medications: Many types of medications can be administered through SC injection, including insulin, allergy medications, anticoagulants, and more.
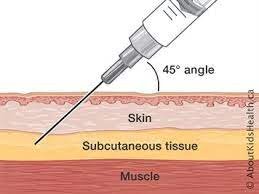
INTRADERMAL INJECTION
An intradermal (ID) injection is a medical procedure in which a small amount of a substance, typically a test substance or vaccine, is injected into the top layers of the skin, known as the dermis. This route of administration is used for diagnostic purposes, skin testing, and specific vaccinations. Intradermal injections are often used when a strong local response is needed, such as in allergy testing or tuberculosis (TB) skin tests.
Medications: Many types of medications can be administered through ID injection, including Tuberculosis (TB) Skin Test, Allergy Testing, Smallpox Vaccination, and more.

HAND WASH
Hand hygiene is a crucial aspect of infection prevention and control in medical settings. Proper hand washing helps to reduce the spread of harmful microorganisms and the risk of infections.
- Wet Your Hands: Use clean, running water to wet your hands. The temperature can be warm or cold.
- Apply Soap: Apply enough soap to create a good lather. This helps to lift dirt, germs, and contaminants from your skin.
- Rub Palms Together: Rub your palms together vigorously to spread the soap and create friction.
- Interlace Fingers: Interlace your fingers and rub the spaces between them on both hands. This includes the area under your nails.
- Rub Backs of Hands: Rub the back of one hand with the palm of the other hand. Switch hands and repeat.
- Rub Between Fingers: Rub the fingers of one hand in between the fingers of the other hand. Repeat for the other hand.
- Rub Fingertips: Grab one hand’s fingers with the opposite hand and rub in a circular motion. Repeat for both hands.
- Clean Your Thumbs: Clean your thumbs by rubbing them using the opposite hand in a rotational manner.
- Clean Your Wrists: Scrub your wrists with both hands by moving them in a circular motion.
- Rinse: Hold your hands under clean, running water to rinse away soap and debris.
- Dry Your Hands: Use a clean towel or air dryer to dry your hands thoroughly. Drying is important to remove any remaining contaminants.
- Turn Off Faucet: Use a clean towel, tissue, or your elbow to turn off the faucet. This helps to avoid recontaminating your clean hands.
- Optional Hand Sanitizer: If soap and water are not available, you can use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer containing at least 60% alcohol. Apply a sufficient amount and rub your hands together until dry.

